|
EXA TEST«
IntraCellular
Diagnostics, Inc«
|
|
|
IntraCellular Diagnostics, Inc.«
Analytical Scanning
Electron Microscopy and Nano Analysis
Office based 60 seconds, non-invasive, specimen collection
Direct Testing For Vital Mineral Electrolytes In The Cell:
Order a Specimen Collection Kit
Order a
Specimen 60
Second Specimen
Published
Research &
|
The Symptoms Complex and The Pharmacology Of Magnesium
The technical information in
this web site is not intended to recommend treatment or make specific
diagnosis based on such data. It is intended for professional informational
purposes, from current medical literature, to assist practitioners in
choosing appropriate protocols and modalities. Decisions on patient care
should be based on all laboratory tests, health histories and clinical
evaluations. The information below was chosen because it is educational and easy to read for both the professional and general public.
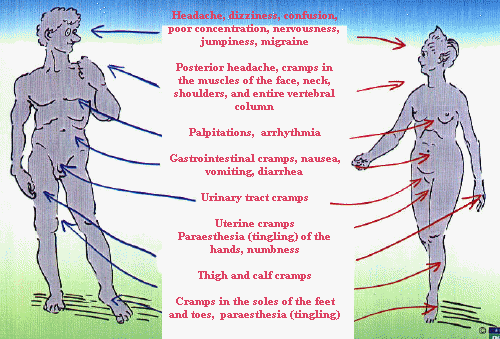
The complex symptomatology Magnesium deficiencies may be observed in
the most diverse forms, ranging from migraine attacks to the unpleasant plantar and toe
cramps.
Magnesium Supplementation under Medical Supervision A distinction is made between two different forms of oral magnesium supplements:
2. Utilization of the pharmacological properties ( no magnesium deficiency) A distinction is made between two different forms of oral magnesium intake. Firstly, replacement therapy, in order to compensate for deficiency. And, high dose magnesium administration, which takes advantage of the pharmacological effects of the mineral, independently of magnesium deficiency.
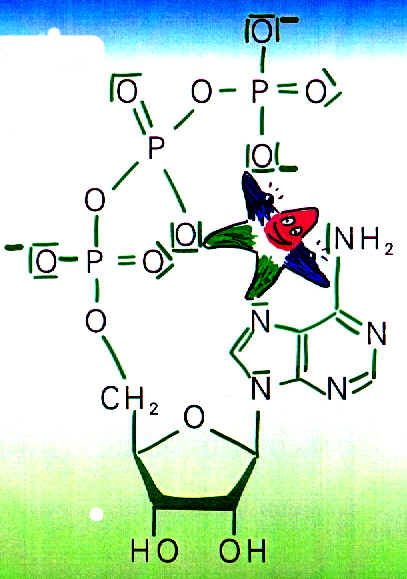
The Pharmacology Of Magnesium As a bivalent cation, magnesium tends to form chelates (from the Greek chele = crabs claws). The most important intracellular binding partner is ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Via chelation, large number of ATP-dependent enzymes, i.e. which promote cellular metabolism, are activated.
The First Effect Of Magnesium Its enzyme cofactor function
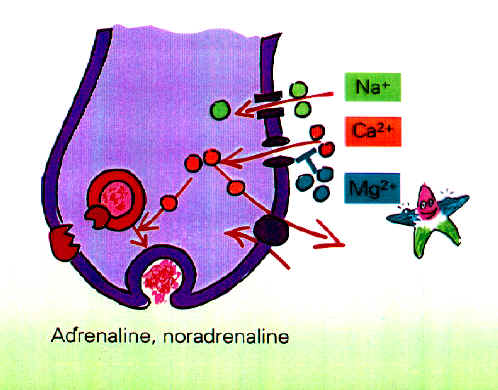
The magnesium ATP complex Owing to the magnesium ATP complex, magnesium acquires a decisive influence over metabolic reactions which use and supply energy. What is more, since the membrane-bound sodium-potassium pump is ATP-controlled, the electrolyte balance of all cells is dependent on magnesium. There is nevertheless scarcely any outside influence on this intracellular effect, which is therefore not in the foreground of pharmacodynamic considerations.
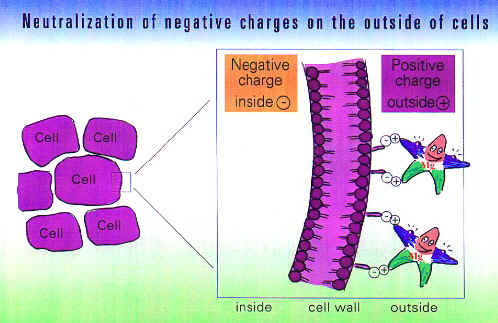
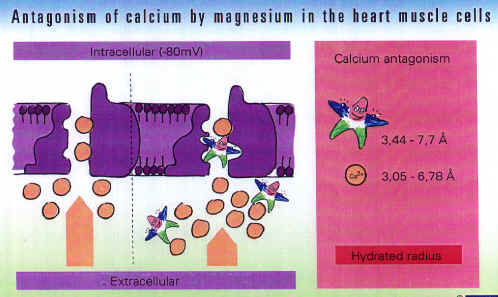
The Second Effect Of Magnesium Neutralization of negative charges The extracellular effect of chelation is, however, interesting: the bivalent, positive magnesium neutralizes negative charges on the outer side of the cells, thereby increasing the potential difference between the inner and outer side of the cell membrane. Pharmacological effects: Calcium antagonism The magnesium ion (Mg 2+ ) is larger, in its hydrated state, than the calcium ion (Ca2+ ) and is therefore capable of displacing the latter. This calcium antagonism acts centrally on both muscle and nerve cells: the magnesium ion occupies the calcium binding sites on muscle cells, thereby displacing calcium into the calcium channel without undergoing the same migration itself. Pharmacological effects: The Fourth Effect Of Magnesium Inhibition by Magnesium of the Release of Neurotransmitters Inhibition of calcium - induced neurotransmitter release Magnesium inhibits calcium - induced neurotransmitter release at the nerve cell level, or to be more precise, at the level of the presynaptic membranes of the sympathetic nervous system. Pharmacological effect:
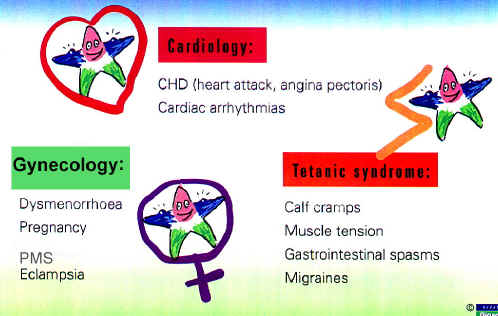
The Use Of Magnesium Indications for magnesium The area of application for magnesium has always been derived from its pharmacology, the muscle and muscle cell:
IntraCellular Diagnostics, Inc« 945 Town Centre Dr. Suite A Medford, OR 97504 Tel. (541) 245-3212 Email us:
ęCopyright IntraCellular Diagnostics, Inc« 2012. All rights reserved. |
|

 1. Substitution therapy
(magnesium deficiency)
1. Substitution therapy
(magnesium deficiency)